Gitds-flow Explanation Work Flow
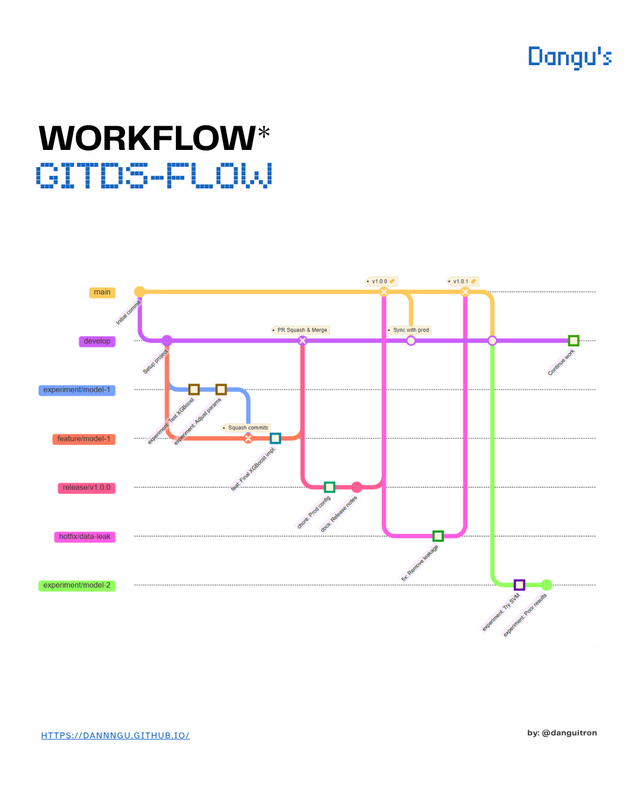
Detailed description of the gitds-flow work flow
- (Init): Repository with two principal branches: ⚛️
main(production) and 🧪dev(development). - New development:
- If it is a hotfix: Branch from
main. - If it is an experiment/feature: Branch from
dev.
- If it is a hotfix: Branch from
- Work in temporary branches:
- Experiments: Tests with the possibility of failure (
experiment/) - Features: Stable development (
feature/). - Hotfixes: Urgent fixes (
hotfix/).
- Experiments: Tests with the possibility of failure (
- Success decision:
- ✅ If the experiment works: Convert to
feature/and PR todev. - ❌ If it fails: Delete branch without merge.
- ✅ If the experiment works: Convert to
- Strategic merge:
- In
dev: Use Squash & Merge for a clean history. - In
main: Use Merge Commit to maintain context.
- In
- Strategic merge:
- Create
release/branch fromdevto prepare release. - Merge to
mainwith semantic tag (v1.0.0).
- Create
- Synchronization:
- After every change to
main, updatedevwithgit merge main.
- After every change to
🗝️ Key Rules
- Temporary branches:
feature/*,experiment/*,release/*,hotfix/*→ Delete after merge.
- Semantic tags:
- Only in
main, usingvMAJOR.MINOR.PATCHformat.
- Only in
- Branch protection:
mainanddevblocked for direct merges (via PR only).
Complete flow with Cookiecutter 🍪
Install Cookiecutter and Create Project
1
2
pipx install cookiecutter-datascience
ccds
Generated Structure
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
my_ds_project/
├── data/
│ ├── raw/ # Raw data (immutable)
│ ├── processed/ # Transformed data
│ └── external/ # Third party data
├── models/ # Trained models
├── notebooks/ # Jupyter/Quarto Markdown
├── src/ # Modular code
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── data/ # Processing scripts
│ └── visualization/ # Viewing scripts
├── docs/ # Documentación
├── .gitignore # Files to ignore
├── requirements.txt # Dependencies
└── README.md # Project Description
Initialize Git Repository and Connect to GitHub 🐈⬛
- Local → New Repository
1 2 3 4
cd my_ds_project git init git add . git commit -m "(init): Project structure with Cookiecutter"
- Create Repository on GitHub
- Go to GitHub → “New repository”.
- Name:
my_ds_project - Do not initialize with
README.md,.gitignore, or license.
- Connect and Upload
1 2 3
git remote add origin https://github.com/tu-usuario/my_ds_project.git git branch -M main git push -u origin main
Configure Main Branches: main and dev 🪴
- Create Branch
dev1 2
git checkout -b dev git push -u origin dev # Upload to remote github
- Protect root branches
mainanddev- Go to your repository → Settings → Branches.
- Click Add branch protection rule.
- Configure for
mainanddev:
- ☑️ Require a pull request before merging.
- ☑️ Require approvals (e.g: at least 1 approval).
- ☑️ Require status checks to pass (if you use CI/CD like GitHub Actions).
- ☑️ Include administrators (so that no one can break the rules).
Daily Workflow (Example with Predictive Model) 🤖
New Feature - (Ex: Train Model)
Step 1: Create Branch from dev
1
2
3
git checkout dev
git pull origin dev
git checkout -b feature/random-forest-model
Step 2: Work and Make Commits
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
# Example of changes:
# - Modify src/models/train_model.py
# - Add notebooks/random_forest.ipynb
git add src/models/train_model.py notebooks/random_forest.ipynb
git commit -m "feat: Add Random Forest classifier with hyperparameter tuning"
git push -u origin feature/random-forest-model
Step 3: Create Pull Request (PR)
- On GitHub, go to “Pull Requests” → “New Pull Request”:
- Base:
dev - Compare:
feature/random-forest-model
- Base:
- Title: “feat: Add Random Forest model with 85% accuracy”
- Description:
1
2
3
4
5
6
## Changes
- Implement Random Forest with GridSearchCV.
- Add evaluation metrics (precision, recall).
## How to Validate
1. Run `python src/models/train_model.py --data-path data/processed/train.csv`
Step 4: Update the dev branch and continue working until you have a release build for PR on the main branch
1
git pull origin dev # To update dev branch to the new changes.
Experiments - (Ex: Test Neural Network)
Step 1: Create Branch from dev
1
2
git pull origin dev # Make sure you have the latest version
git checkout -b experiment/cnn-model # Create experiment branch
Step 2: Work and Make Commits
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# If the experiment fails after several commits:
# Modify code/notebooks...
git add notebooks/cnn_experiment.ipynb
git commit -m "experiment: Test CNN with 3 convolutional layers"
# Keep iterating...
git add src/models/cnn.py
git commit -m "experiment: Add dropout layers to prevent overfitting"
Step 3a: If the Experiment Fails: (e.g: accuracy < 70%)
1
2
3
4
# Delete local and remote branch:
git checkout dev
git branch -D experiment/cnn-model # Delete local branch
git push origin --delete experiment/cnn-model # Delete remote branch (if uploaded)
Step 3b: If the Experiment is Successful: (e.g: accuracy > 85%):
1
2
3
4
5
# Rename branch to feature/ and create PR:
git checkout dev
git branch -m experiment/cnn-model feature/cnn-model # Rename local
git checkout feature/cnn-model
git push origin -u feature/cnn-model # Upload the renamed branch
Step 4: Create Pull Request (PR) to dev
- On GitHub:
- Title:
feat: Add CNN model with 85% accuracy. - Description:
- Title:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
## Changes
- Implement a CNN with dropout layers.
- Accuracy of 85% in validation data.
## How to test
python src/models/train.py --model cnn
- Reviewers: Assign another team member (if any).
Step 5: Merge to dev
- Strategy: Squash and Merge (merges all the experiment’s commits into one). GitHub does this automatically when you click “Squash and Merge.”
- Result: A single commit in
dev:feat: Add CNN model with 85% accuracy.
[!INFO] Why
--squash?
- Merge all the experiment’s commits into one, keeping the branch
devhistory clean.
Step 6: Update the dev branch and continue working until you have a release build for PR on the main branch
1
git pull origin dev # To update dev branch to the new changes.
Releases - Bring Changes to Production (Merge to main)
Step 1: Create release/* branch from dev
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
git checkout dev
git pull origin dev
git checkout -b release/v1.0.0
# Make final adjustments (e.g: parameters, documentation)
# Example: Adjust thresholds for production
git add src/models/cnn.py
git commit -m "feat: Adjust prediction thresholds for production"
# Update documentation
git add docs/model_deployment.md
git commit -m "docs: Add CNN deployment steps"
Paso 2: PR to main
1
git push -u origin release/v1.3.0
- PR Title:
(release): CNN model v1.3.0. - Description:
1
2
3
## Changes
- Modelo CNN listo para producción.
- Documentación actualizada.
- Mergear: Usar Merge Commit (no squash) para mantener el contexto de la release.
Step 3: Merge to main and Create Tag
1
2
3
4
git checkout main
git merge --no-ff release/v1.0.0 # Mantener historial
git tag -a v1.0.0 -m "(release): First production model Random Forest"
git push origin main --tags
Step 4: Update dev
1
2
3
git checkout dev
git merge main # Synchronize with latest changes
git push origin dev
Step 5: Update main to the last release changes
1
git pull origin main
Hotfixes - (Production Errors)
Problem: The model in main (v1.3.0) has a division by zero error.
Step 1: Create branch from main
1
2
3
git checkout main
git pull origin main
git checkout -b hotfix/division-error
Step 2: Correct and Commit
1
2
3
git add src/models/cnn.py
git commit -m "(hotfix): Handle division by zero in loss calculation"
git push -u hotfix/division-error
Step 3: PR to main and Tag
- Merge with Rebase and Merge (for linear history).
- Tag:
1 2
git tag -a v1.3.1 -m "(hotfix): Division by zero error" git push origin --tags
Step 3: Merge to main and synchronize dev
1
2
3
git checkout dev
git merge main # Bring the hotfix to develop
git push origin dev
Step 4: Update main to the last release changes
1
git pull origin main
Reflection Q&A
[!faq] Why This Flow?
- Disposable Experiments: If they fail, they do not contaminate the
devhistory. - Squash in PRs: Combine multiple experiment commits into one clean one (avoid noise in
dev). - Semantic Tags: Clear versions in
mainfor rollbacks or audits. - Update
dev: After each release,devis synchronized withmainto include hotfixes.
Cheat Sheet Advanced
Commands for Branch Management
| Action | Command |
|---|---|
Create branch from dev/ |
git checkout -b feature/nombre dev |
| Rename branch | git branch -m old-name new-name |
| Do squash in PR | Click en “Squash and Merge” en GitHub |
Synchronize dev/ with main/ |
git checkout dev && git merge main |
Sync branch with dev/ |
git pull origin dev |
| Force local delete | git branch -D branch-name |
| Delete remote branch | git push origin --delete branch-name |
Commands for Tags
| Action | Command |
|---|---|
| Create tag | git tag -a v1.0.0 -m "Message" |
| Upload tags | git push origin --tags |
| Delete local tag | git tag -d v1.0.0 |
| Delete remote tag | git push origin :refs/tags/v1.0.0 |
Commands for Data (DVC)
| Action | Command |
|---|---|
| Version a dataset | dvc add data/raw/dataset.csv |
| Upload data to storage | dvc push |
| Recover a version | dvc checkout data/raw/dataset.csv |